
CSIR-IHBT
IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY FIBROSIS INFORMATION PORTAL
(A Molecular Systems Database for IPF)
IPFIP is a firstever dynamics portal based on molcular study in Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. It is highly interactive to view the insight of IPF disease.
There is no high-throughput data repository of IPF till date containing systematic molecular information. Molecular, genomic and system data, and other information on IPF are scattered. To overcome this problem, a portal was designed with detailed information on IPF and its molecular system, named as IPF Information Portal (IPFIP).
A search section is available with quick query search for genes/miRNAs/TF/pathways in IPF. Two is the minimum limit of characters in the search box to invoke the auto-suggested results fetched from the MySQL database of genes table in the form of json based structure through PHP script.
Results of query are displayed in three tables. The first table provide the detailed information of genes including chromosomal location, KEGG/wiki/PathwayCommons information, associated gene ontology information, differentially expressed gene status and options to locate the genes in regulatory networks and PPI networks. The second table displays the information about the involvement of transcription factors, TF target genes with anti-correlation and interaction support between the TF and target gene. The third table visualizes the information if a query gene is targeted by any miRNA. In the third table, information about miRNA and target gene with anti-correlation/experimental support is displayed. All above mentioned tables are linked with network graphs within the portal hosting network status.
The second part of search section is available for browsing IPF involved miRNAs, hierarchal pathway involvement and crosstalk pathway information. miRNAs in IPF tab is provided to search the detailed information of each miRNAs along with its miRNA-gene pair interaction. User can perform the comparison between two selected miRNAs in similar expression pattern only. Other useful information is displayed about the selected miRNA along with the user selected comparable miRNA on the basis of average expression in form of line chart. A venn diagram displays the target genes of the selected miRNA and user compared miRNA based on average expression and shows the common and exclusive target sets. A tree chart of miRNA target genes is displayed by clicking on miRNA square shaped node. Additionally, target analysis tab performs gene and pathway enrichment analysis of selected miRNAs separately as well as common target genes, if any.
Hierarchal pathways information regarding IPF influenced by DEGs is incorporated in the tab entitled as Pathways in IPF. Circular tree chart is visualized with red and green nodes of pathway. The red color nodes indicate downregulated pathways while green nodes represent upregulated pathways. Each parent pathway node is connected to its child nodes in the form of parent-child relationship. Such type of relation shows that the parent and child pathway sharing common genes in relationship. Each parent and child node is available with mouseover effects in the form of tooltip. It provides the option to view the gene in KEGG pathway in red color box. User has option to zoom in/out the circular pathway tree in the browser area.
The Pathway Crosstalk tab is designed to view the pathway crosstalk information of IPF involved pathways. Each major pathway node is further related to the child node (crosstalk) showing cross relationship between two pathways through the interaction of DE genes. Each node of tree is configured with mouseover tooltip option for KEGG pathway mapping, retrieval of information about crosstalked genes and option to get gene enrichment. Another option is provided to visualize crosstalked pathways simultaneously with information of DE genes status as downregulated (red colored down arrow) or upregulated (green colored up arrow) in form of table.
The network list menu bar option provides sub-list of regulatory and PPI networks for the three DEG sets considered in the study. In regulatory network, the involvement of miRNAs, TF, and genes is shown in different colours and with different shapes of nodes as well as varying width of edges. Triangle shaped red and green nodes for the miRNAs, square shaped orange and blue coloured for the TF genes and circular shaped light green and light red coloured nodes for DE genes. Top side of the network visualization page provides facility to locate desired node in network. Network graph also implements mouseover effects like tooltip which shows the network properties including number of interacting nodes, average path length, betweenness, closeness centrality, indegree, outdegree etc. Network properties table is also provided along with network graph tab. Interacting partners of hover node can be displayed on double clicking which dynamically hide other nodes in the graph.
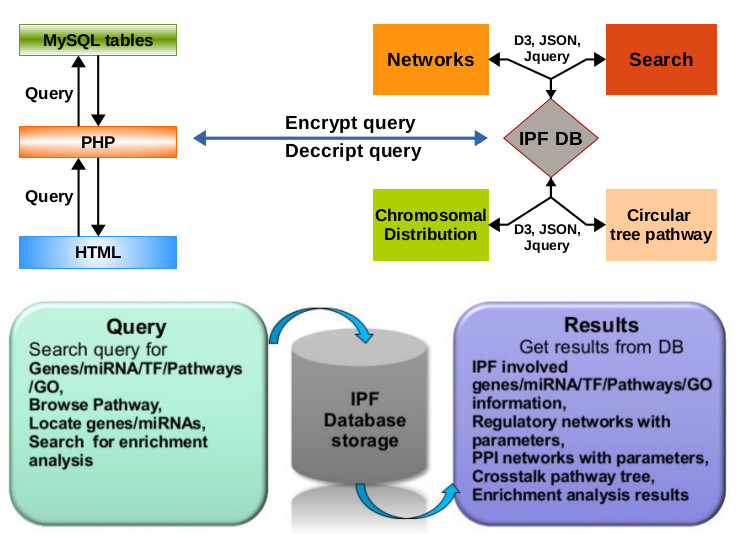
Further single clicking on node appends the respective node into a text area for further analysis like pathway enrichment and gene enrichment. Pathway enrichment analysis is done by Enrichr web server whereas gene enrichment is performed by in-house built R script using hyper-geometric test followed by the bonferroni corrected p-value. Another utility is available to search and locate genes, miRNAs and TFs in graph which is helpful for user to retrieve network status of their gene of interest. Gene expression based classification of IPF utility considers the IPF sample data with expression values and displays the number of samples classified as IPF using SVM in the background with PHP interface. The architecture and workflow of IPF portal is provided in Fig 14. The systematic representation of each section is described in a meaningful way to understand the mechanistic view of IPF disease. Also the portal hosts the associated data from this study. The IPF portal is available at /ipf and http://scbb.ihbt.res.in/software.php.
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, pathological form of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia, is a chronic, progressive, irreversible, and usually lethal lung disease. IPF is classified as rare disease, and occurs in middle-aged and elderly adults. Among densely populated countries Brazil, China, Russia and India approximately 2 million persons living with IPF. Advancement have been made in understanding the pathogenesis of this disease.
Phenotypic alteration of alveloar epithelial cells attains a honey comb structure as the centralized feature of the IPF and with the continuos damage leads to the fibrotic scarring. As the disease progresses, alveolar-capillary units are impacted, oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange is impaired, ultimately leading to respiratory failure. The reason behind the initiation of fibrotic cascade is still not known. There are numerous treatment options are available but yet no cure has been discovered.
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is the one of the rarest form of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias(IIP). Characterization of IPF is done by the impaired lung architecture (honey comb structure and irreversible scarring) with excessive accumulation of collagen and ECM formation.
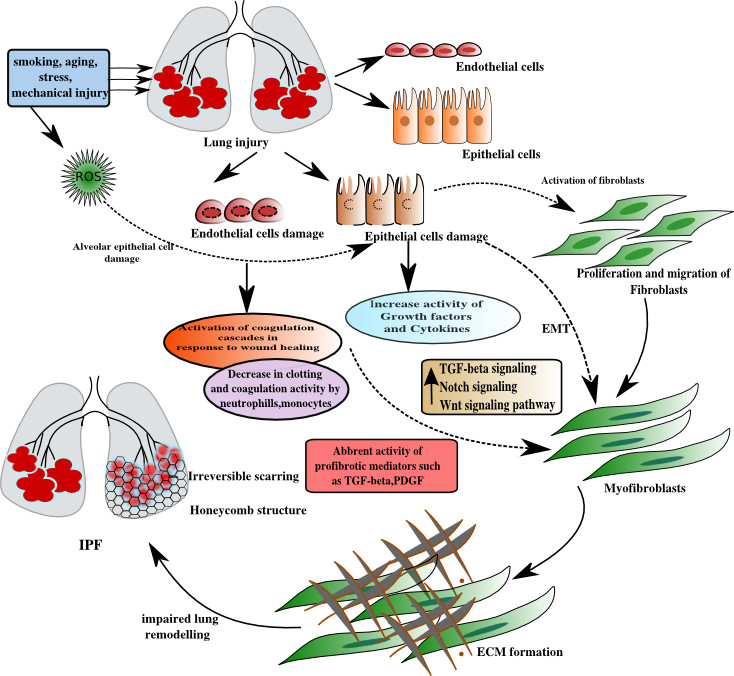
- Induction of IPF involved lung injury. Smoking, aging, stress and mechanical injury are considered to be major factors for lung injury.
- Primary lesions of injury are initiated with endothelial and epithelial cell damage. ROS activity is also induced with lung injury and results in increase in oxidative stress.
- Normally,in order to counteract the damage occurred to endothelial cells, coagulation cascades became active to provide a defensive action against injury. Neutrophills, monocytes , basophillls are the major players of coagulation cascades. In IPF, this defensive force fails to restore endothelial cell damage .
- Damage to epithelial cells leads to the activation of fibroblasts. This damage enhance the antifibrotic activity of growth factors and cytokines to reduce the proliferation and migration of fibroblasts into myofibroblasts. In IPF, the antifibrotic activity is replaced by the abbrent activity of profibrotic mediators ( TGF-beta , PDGF ) which results in upregulation of TGF-beta signaling pathway, Notch signaling pathway, Wnt signaling pathway. This upregulation of pathways promotes the EMT transitions, along with proliferation of fibroblasts which results in formation of myofibroblasts.
- Myofibroblasts proliferation leads to the increment in ECM formation, which is marked by increased epithelial cell apoptosis and reduction in myofibroblast apoptosis.
- Continuation of ECM formation leads to its accumulation which impaired the lung architecture.