
(Causal Transcription Factor- Bayesian Integration of Network Dynamics)


(Causal Transcription Factor- Bayesian Integration of Network Dynamics)
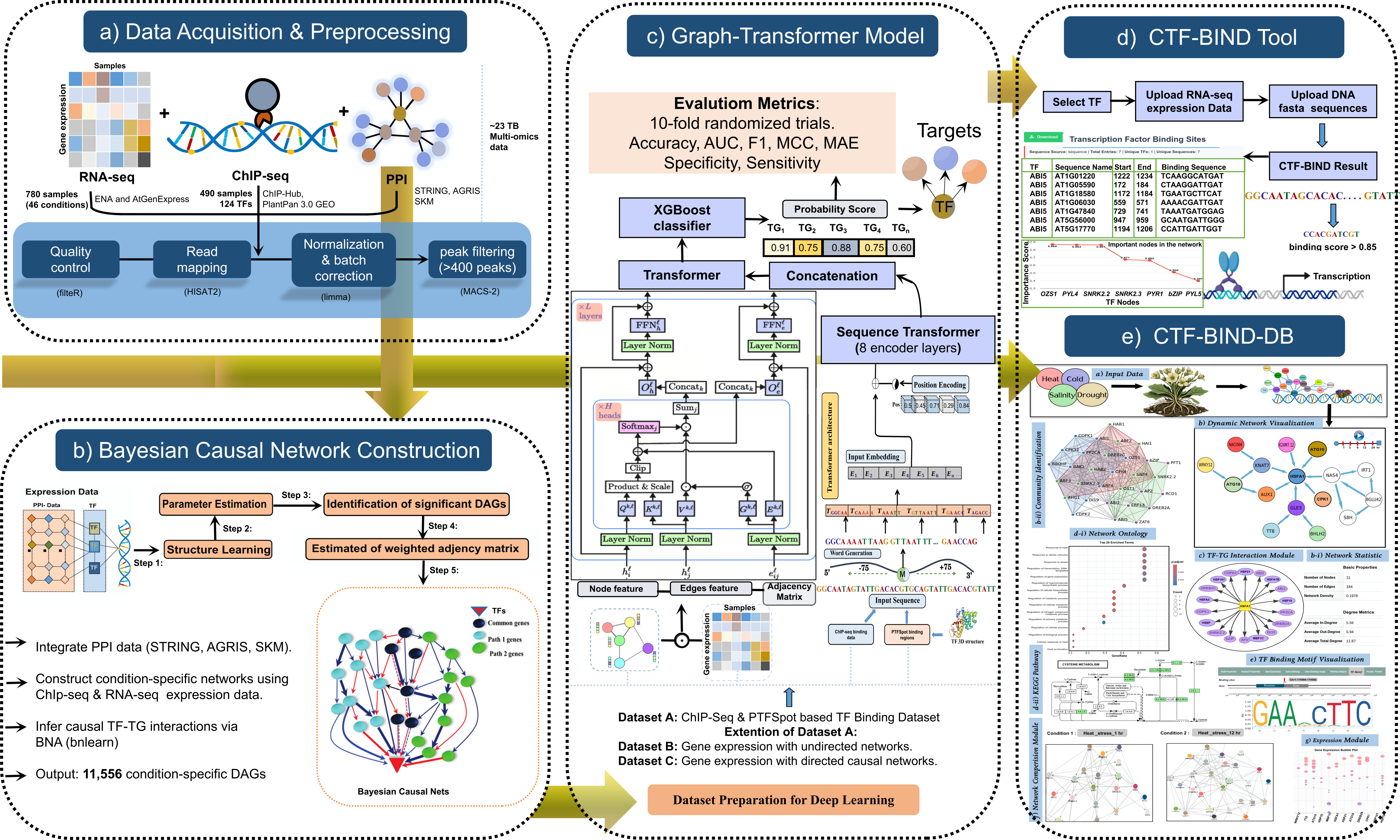
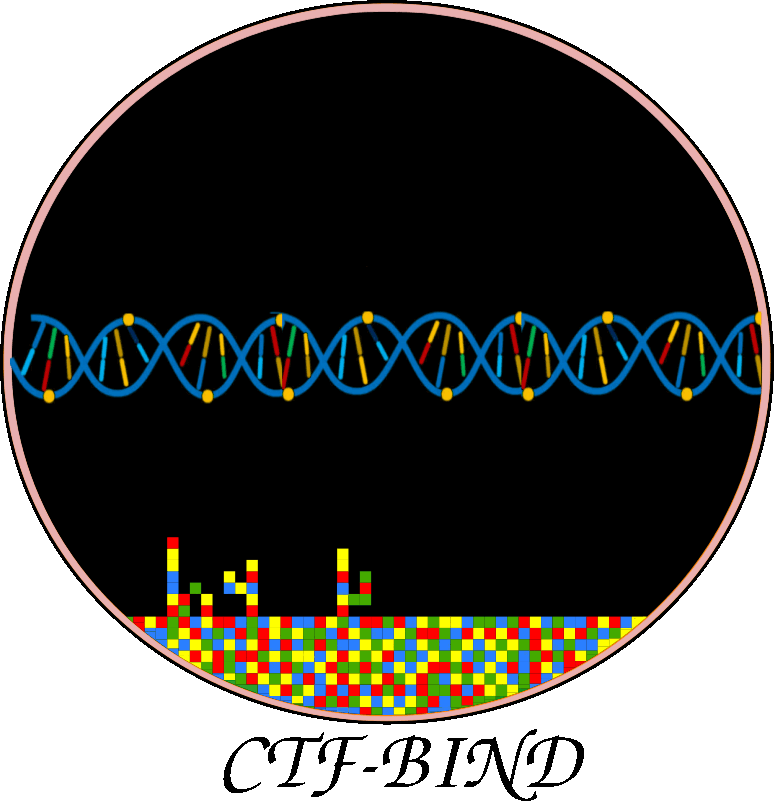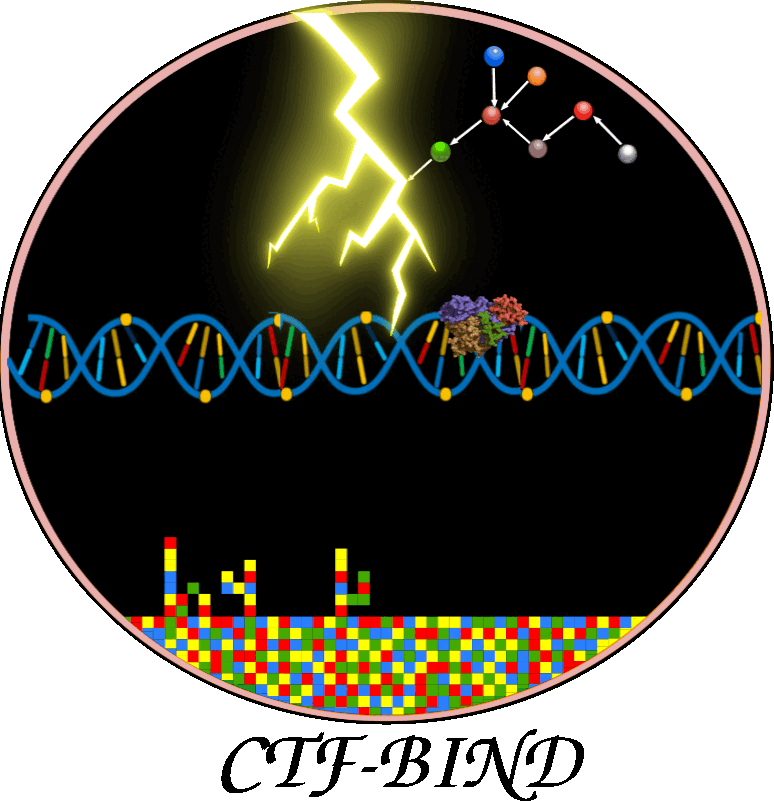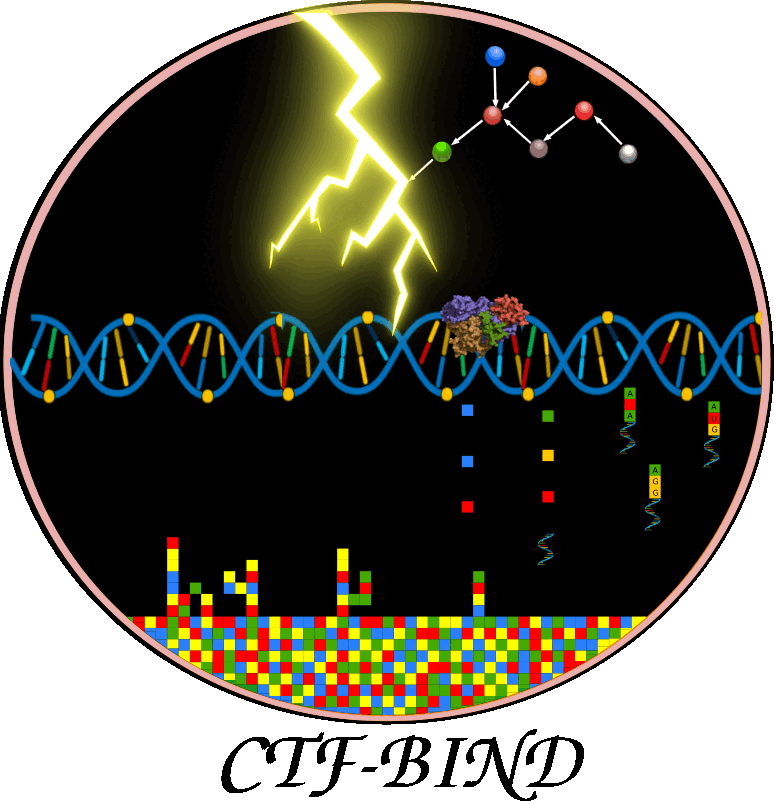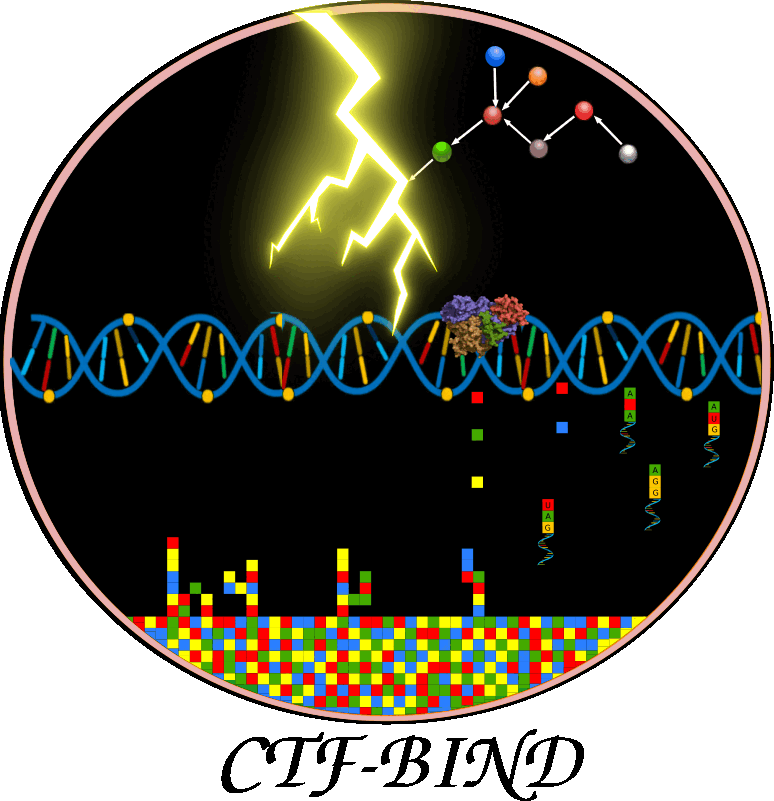
This figure illustrates CTF-BIND, a causality-aware Graph-Transformer deep learning model for predicting stress-specific transcription factor (TF)-DNA binding. a) Data Acquisition & Preprocessing: This panel shows the initial steps, collecting RNA-seq, ChIP-seq, and Protein-Protein Interaction (PPI) data. All data undergoes a rigorous quality control, mapping, normalization, and batch correction. ChIP-seq data is filtered to include only high-quality samples with over 400 identified peaks. b) Bayesian Causal Network Construction: This section details the inference of causal TF-Target Gene (TG) interactions. PPI data is integrated, followed by structure learning and parameter estimation using ChIP-seq and RNA-seq data to construct condition-specific gene regulatory networks. Bayesian Network Analysis (BNA) identifies significant DAGs, resulting in 11,556 condition-specific causal networks. c) Graph-Transformer Model: This panel outlines CTF-BIND's deep learning architecture. Datasets are prepared from ChIP-seq, PPI, and expression data, including undirected and directed causal networks. The model combines a Sequence Transformer (8 encoder layers) for DNA features with a Graph Transformer for network features. Their concatenated output feeds into an XGBoost classifier to predict TF-DNA binding probabilities. Performance is evaluated using 10-fold cross-validation with metrics like Accuracy, AUC, and MAE. d) CTF-BIND Tool: This panel demonstrates the user interface, allowing users to select TFs, upload RNA-seq expression and DNA sequence data, to obtain predicted target genes with binding scores. e) CTF-BIND-DB: This panel highlights the integrated database, providing a resource for visualizing TF-gene regulatory networks and specific DNA binding motifs, aiding in the analysis of stress-specific transcriptional regulation.
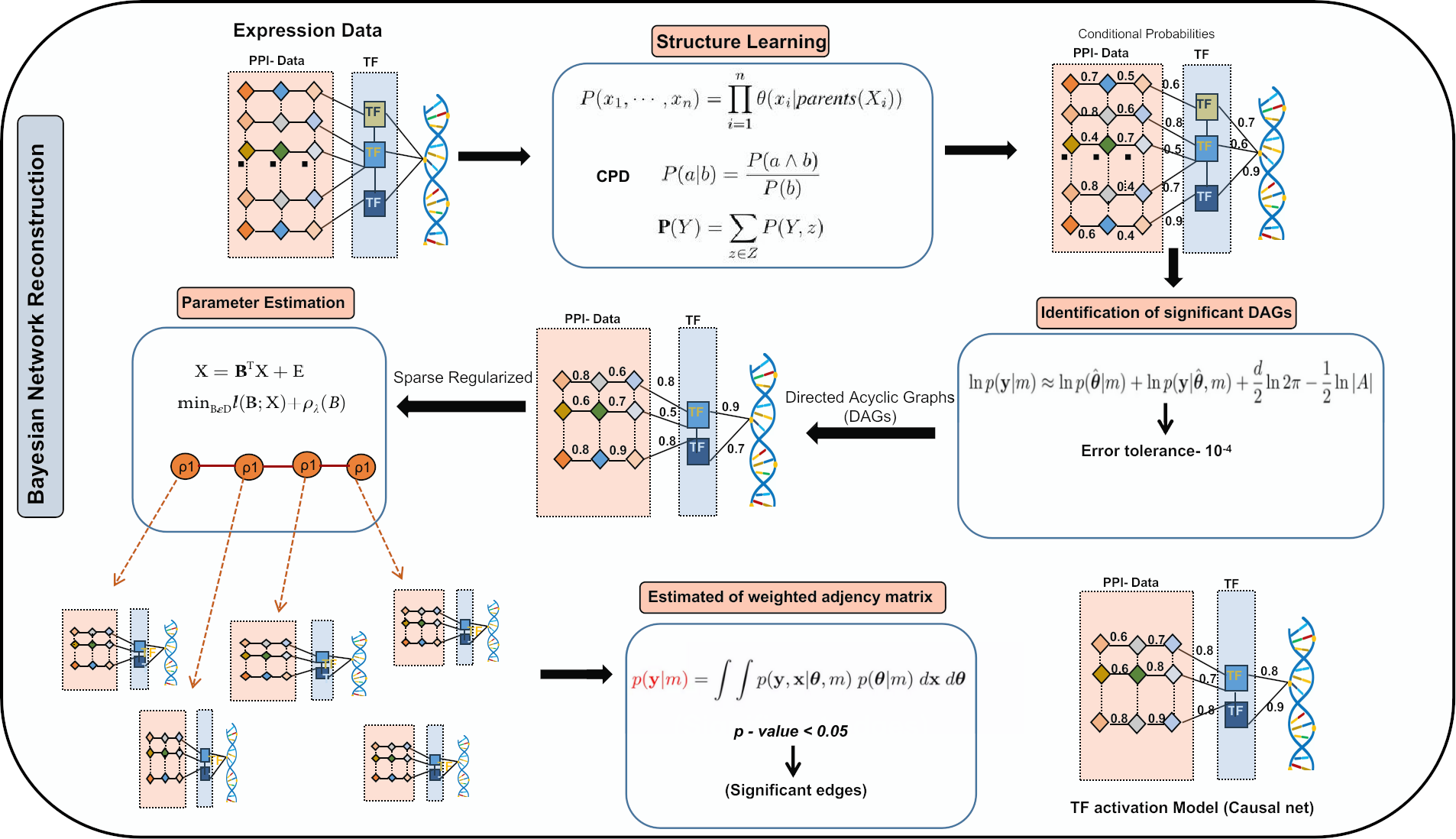
Steps in Bayesian network reconstruction. The process involves: 1) Estimation of Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs) between target genes (TGs), transcription factors (TFs), and their protein-protein interaction (PPI) partners using expression data and prior knowledge. 2) Identification of significant DAGs based on convergence criteria. 3) Modeling of significant DAGs with a generalized linear model assuming a multivariate Gaussian distribution. 4) Parameter estimation between TGs, TFs, and PPI partners using sparse regularization. 5) Selection of the optimal regularization penalty based on different rho lambda values. 6) Final parameter estimation using the optimal penalty and criteria-based parameter selection.
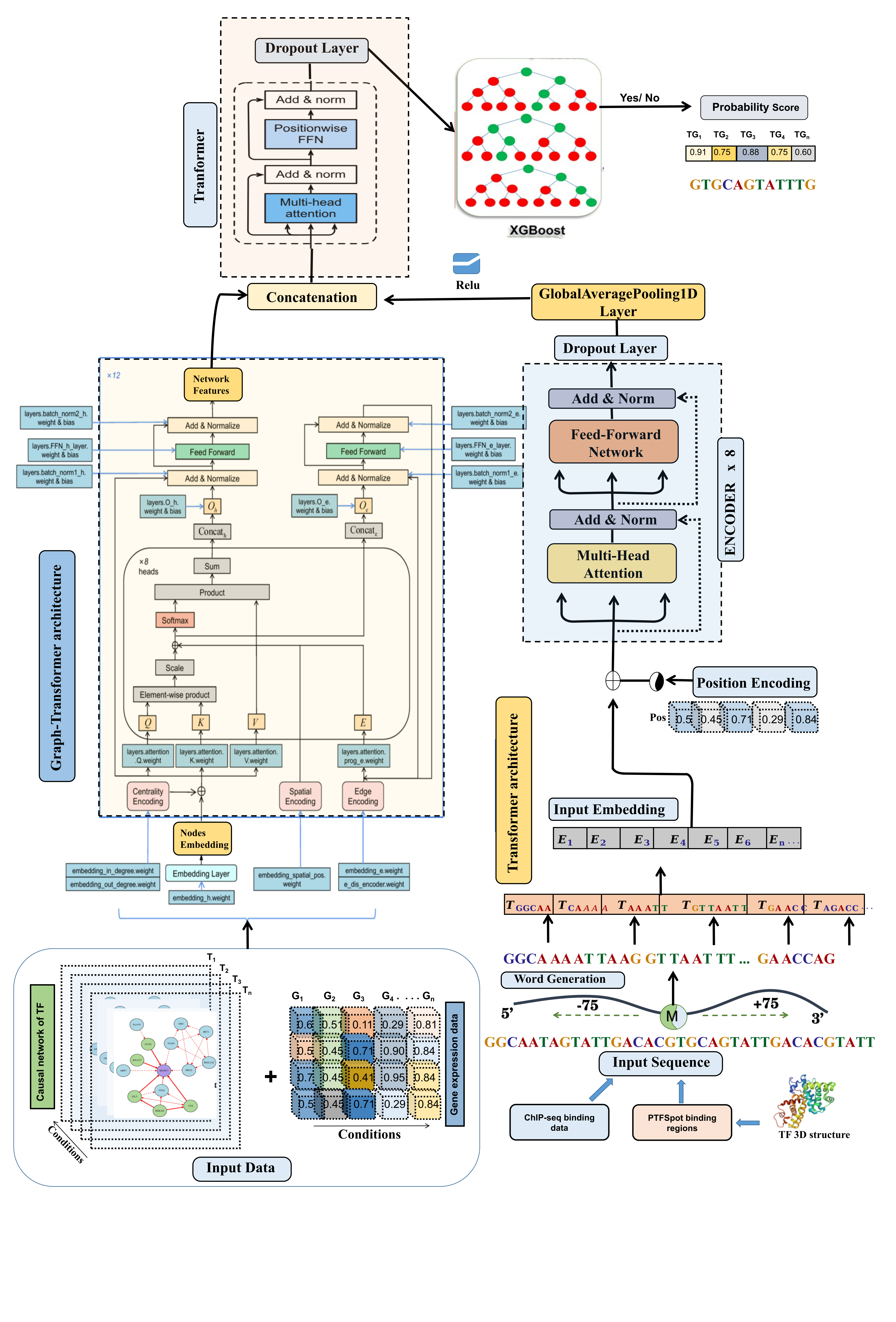
Overview of the architecture and workflow of the CTFBind framework for predicting transcription factor (TF) binding activity. Input data includes TF causal networks, gene expression profiles, ChIP-seq data, TF 3D structures, and promoter sequences. A Graph-Transformer processes network features, while a Transformer encodes DNA sequence information.

This figure illustrates how CTF-BIND enables accurate TF binding predictions directly from transcriptome data, eliminating the need for additional ChIP-seq experiments.Application of CTF-BIND on RD29A gene as a case study with implementation of web-server. .